We serve 4-Fluoropyridine CAS:694-52-0 to global customers since 2007, Pls send inquiry to info@nbinno.com or visit www.nbinno.com our official website should you have any interests. This site is for information only.
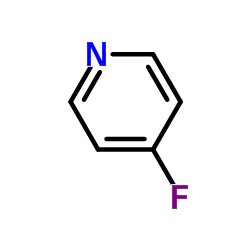
Contact us for information like 4-Fluoropyridine chemical properties,Structure,melting point,boiling point,density,molecular formula,molecular weight,Pyridine,4-fluoro physical properties,toxicity information,customs codes,safety, risk, hazard and MSDS, CAS,cas number,4-Fluoropyridine Use and application,4-fluoro-pyridine technical grade,usp/ep/jp grade.
Related News: There is fierce competition for bulk APIs and overcapacity. However, some high-profit, small-scale drugs still have a good market space.3-Fluoro-4-morpholinoaniline manufacturer The workers are demanding that Hong Kong close all border checkpoints to visitors from mainland China, saying they represent a threat to health care workers in the city.4-methylsulfanylbutan-2-one supplier Among the APIs we produce, there is an API which passes through over ten kinds of intermediates in a process when it changes from being a raw material into an API.2,6-Dichloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)nicotinonitrile vendor Among the APIs we produce, there is an API which passes through over ten kinds of intermediates in a process when it changes from being a raw material into an API.Different cell types can be affected, although the most common finding in MDS is a shortage of red blood cells (anaemia). Patients with higher-risk MDS may progress to the development of acute leukaemia.

