We serve Chemical Name:Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH CAS:198545-76-5 to global customers since 2007, Pls send inquiry to info@nbinno.com or visit www.nbinno.com our official website should you have any interests. This site is for information only.
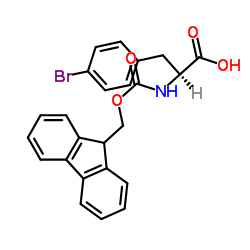
Chemical Name:Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH
CAS.NO:198545-76-5
Synonyms:(r)-n-fmoc-4-bromophenylalanine;L-Phenylalanine, 4-bromo-N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-;Fmoc-L-phe(4-Br)-OH;4-Bromo-N-[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]-L-phenylalanine;FMOC-PBR-D-PHE-OH;AmbotzFAA1681;FMOC-D-4-BROMOPHE;Fmoc-D-Phe(p-Br)-OH;(2S)-3-(4-Bromophenyl)-2-{[(9H-fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl]amino}propanoic acid;MFCD00273459;Fmoc-4-bromo-D-phenylalanine;Fmoc-4-bromo-Phenylalanine;Fmoc-D-phe(4-Br)-OH;Fmoc-D-4-Bromophenylalanine
Molecular Formula:C24H20BrNO4
Molecular Weight:466.324
HS Code:
Physical and Chemical Properties:
Melting point:170-172ºC
Boiling point:660.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
Density:1.5±0.1 g/cm3
Index of Refraction:1.647
PSA:75.63000
Exact Mass:465.057556
LogP:6.18
Material Safety Information (Applicable for Hazard Chemicals)
RIDADR:
Packing Group:
Contact us for information like (r)-n-fmoc-4-bromophenylalanine chemical properties,Structure,melting point,boiling point,density,molecular formula,molecular weight,Fmoc-D-4-Bromophenylalanine physical properties,toxicity information,customs codes,safety, risk, hazard and MSDS, CAS,cas number,FMOC-D-4-BROMOPHE Use and application,(r)-n-fmoc-4-bromophenylalanine technical grade,usp/ep/jp grade.
Related News: The American Heart Association explains that metabolic syndrome — a grouping of five different conditions — elevates the risk for such illnesses. Abdominal obesity is one such condition; the other four include high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high blood pressure and low levels of good” HDL cholesterol.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH manufacturer Beta Bionics is committed to obtaining regulatory approval and commercializing all three iLet configurations. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH supplier The American Heart Association explains that metabolic syndrome — a grouping of five different conditions — elevates the risk for such illnesses. Abdominal obesity is one such condition; the other four include high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high blood pressure and low levels of good” HDL cholesterol.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH vendor The American Heart Association explains that metabolic syndrome — a grouping of five different conditions — elevates the risk for such illnesses. Abdominal obesity is one such condition; the other four include high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high blood pressure and low levels of good” HDL cholesterol.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH factory But even though weight-loss success depends on adopting a challenging” change in post-operation diet and lifestyle, the process can certainly “help people to lose weight and get comorbid [other negative health] conditions under better control,” Sandon said.
So it’s important, she said, to help eligible patients better “understand the treatment options and potential for success,” by sharing surgery success stories and highlighting the benefits of reducing high-risk health issues such as blood pressure and diabetes.
An experimental Alzheimer’s vaccine appears to safely clear abnormal tau protein from the brain, but it’s not yet clear whether the shot will be able to save brain function.
In a Phase 2 clinical trial, the vaccine produced high levels of antibodies to target and attack free-floating tau proteins before they can form “tau tangles” that clog neurons and damage brain function. Tau tangles, along with plaques formed by the protein amyloid-beta, serve as one of the main hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.
“While amyloid influences speed of Alzheimer’s progression, there is strong evidence that tau pathology relates to the underlying cause of the disease,” said lead researcher Dr. Petr Novak, a senior clinical research scientist at AXON Neuroscience, the Slovakian pharmaceutical company developing the vaccine. “Brain atrophy and cognitive loss closely echo the deposition of pathological tau protein, as evidenced by recent tau PET studies.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH manufacturer Beta Bionics is committed to obtaining regulatory approval and commercializing all three iLet configurations. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH supplier The American Heart Association explains that metabolic syndrome — a grouping of five different conditions — elevates the risk for such illnesses. Abdominal obesity is one such condition; the other four include high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high blood pressure and low levels of good” HDL cholesterol.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH vendor The American Heart Association explains that metabolic syndrome — a grouping of five different conditions — elevates the risk for such illnesses. Abdominal obesity is one such condition; the other four include high blood sugar, high triglycerides, high blood pressure and low levels of good” HDL cholesterol.
Bariatric surgery — including sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass — offers an opportunity to reduce such risk by helping patients achieve considerable weight loss, the investigators said.
In fact, the study team noted that bariatric surgery is the standard of care for severely obese patients. Severe obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 40, or a BMI of 35 and up alongside obesity-related complications such as diabetes.
Using insurance claims data, Schimpke and his team focused on a pool of nearly 1.8 million patients across the United States who were severely obese — and therefore eligible for bariatric surgery — in the decade beginning 2010.
Of those, roughly 100,000 actually underwent bariatric surgery during that time frame. But procedure patterns varied widely by state.
For example, while between roughly 9% and 10.4% of eligible patients in New Jersey, Rhode Island and Delaware opted for surgery, less than 3% did so in West Virginia, Alabama and Arkansas.
Overall, the researchers determined that the lowest in opt-in rates by region was the Midwest, where just over 4% of eligible patients underwent surgery, despite the fact that nearly 34% of Midwesterners are obese (making the region home to the highest overall obesity rates in the country).
By contrast, the highest opt-in surgery rate (nearly 8%) was seen in the Northeast region, where the overall obesity rate is lower (29%).
The findings were presented last week at a virtual meeting of the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Such research is considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
“There are likely several contributing factors to the wide variation in utilization,” said Schimpke. He highlighted differences in: levels of access to medical care; beliefs and attitudes among patients and referring physicians; number of available hospitals and surgeons; and insurance coverage requirements.
Schimpke also pointed to the “negative psycho-social connotation associated with bariatric surgery among both physicians/practitioners and patients, which needs to be addressed with strategic campaigns detailing the safety and efficacy of bariatric surgery. Fmoc-D-Phe(4-Br)-OH factory But even though weight-loss success depends on adopting a challenging” change in post-operation diet and lifestyle, the process can certainly “help people to lose weight and get comorbid [other negative health] conditions under better control,” Sandon said.
So it’s important, she said, to help eligible patients better “understand the treatment options and potential for success,” by sharing surgery success stories and highlighting the benefits of reducing high-risk health issues such as blood pressure and diabetes.
An experimental Alzheimer’s vaccine appears to safely clear abnormal tau protein from the brain, but it’s not yet clear whether the shot will be able to save brain function.
In a Phase 2 clinical trial, the vaccine produced high levels of antibodies to target and attack free-floating tau proteins before they can form “tau tangles” that clog neurons and damage brain function. Tau tangles, along with plaques formed by the protein amyloid-beta, serve as one of the main hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.
“While amyloid influences speed of Alzheimer’s progression, there is strong evidence that tau pathology relates to the underlying cause of the disease,” said lead researcher Dr. Petr Novak, a senior clinical research scientist at AXON Neuroscience, the Slovakian pharmaceutical company developing the vaccine. “Brain atrophy and cognitive loss closely echo the deposition of pathological tau protein, as evidenced by recent tau PET studies.

